By Shan Abdul @ HowToGeek
Firefox comes with a range of features you might never use—and may even find annoying. While some nuisances can be turned off in the regular settings menu, others require adjustments on the about:config page—and that approach is often quicker too. Here are a few settings I’ve turned off using it.
Stop Auto-Playing Media
Do you hate it when videos or audio start playing without your consent the moment you open a website? This not only interrupts your browsing but also eats bandwidth and slows down page loading. If you want your browsing to stay distraction-free, Firefox lets you disable the autoplay of media, both video and audio, through the about:config preferences.
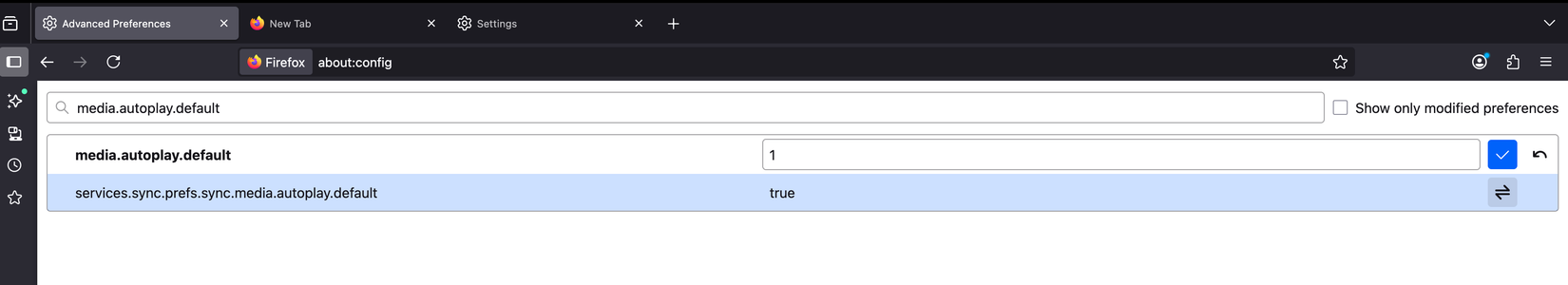
To adjust how Firefox handles media playback, type about:config in the browser’s address bar and open the preferences page. Then, type media.autoplay.default in the search box to locate this preference. Click the pencil icon next to it and change the value from 1 to 5, which instantly prevents videos and audio from playing automatically.
Should you wish to revert this change, you can return here anytime and set the value from 5 to 1 again.
Disable Search Suggestions
When you type something into the address bar, Firefox shows search suggestions pulled directly from your default search engine. While this can save a few keystrokes by predicting what you’re about to type, it also means your data is sent to that engine before you even hit enter—a potential privacy risk. I personally find this concerning.
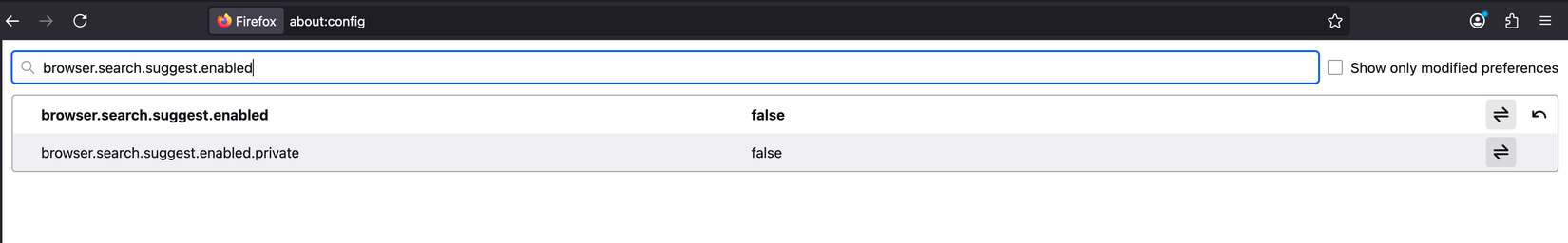
On top of that, suggestions can become a distraction, pulling you toward unrelated queries instead of the task you actually opened the browser for. That’s why I prefer keeping this feature turned off. To turn it off, go to the preferences page, type browser.search.suggest.enabled, and click the switch icon to set it to False.
Get Rid of Extra Animations
Firefox includes built-in animations and effects like tab fade-ins or menu slide-outs, which give the interface a smooth, polished look. While these visuals improve aesthetics, they can also slow down navigation. On lower-end devices, especially, such animations can put extra strain on hardware, making browsing feel sluggish.
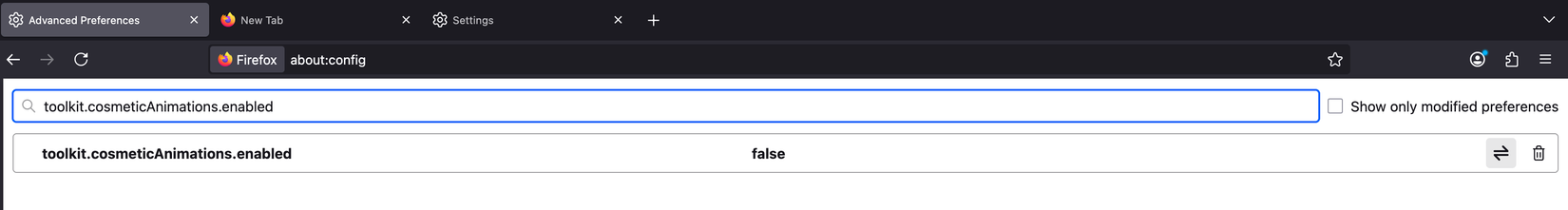
For a faster, more responsive experience where pages, menus, and tabs appear instantly, you should turn these animations off. To do this, open the about:config page in Firefox, search for toolkit.cosmeticAnimations.enabled, and double-click it to switch the value from True to False. Once disabled, you’ll notice a clear improvement in performance.
Turn Off Telemetry and Data Collection
Like most browsers and operating systems, Firefox collects some diagnostic and usage data, often referred to as telemetry. It does this to troubleshoot existing bugs, improve the performance of the browser, and add new features.
Although it's claimed that this data is anonymized, I'm not comfortable sharing details about my browsing habits. If you're a privacy-conscious user, you should turn off this feature to gain better control over the data leaving your system.
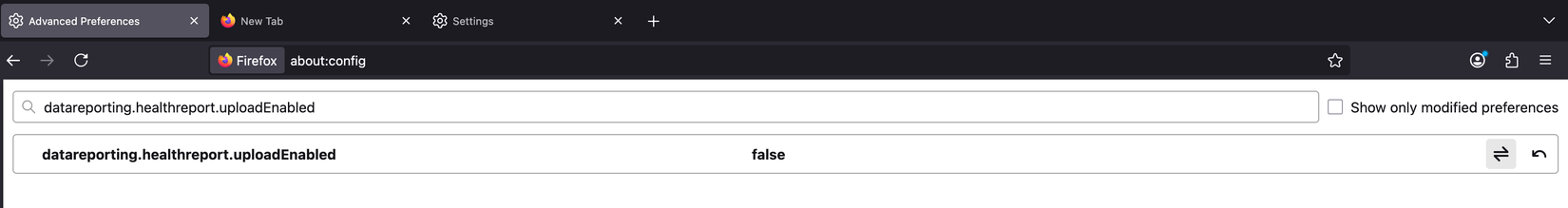
To turn off telemetry and data collection in Firefox, locate the following entries in about:config and set their values from True to False:
- Toolkit.telemetry.enabled
- Toolkit.telemetry.unified
- Browser.ping-centre.telemetry
- datareporting.healthreport.uploadEnabled
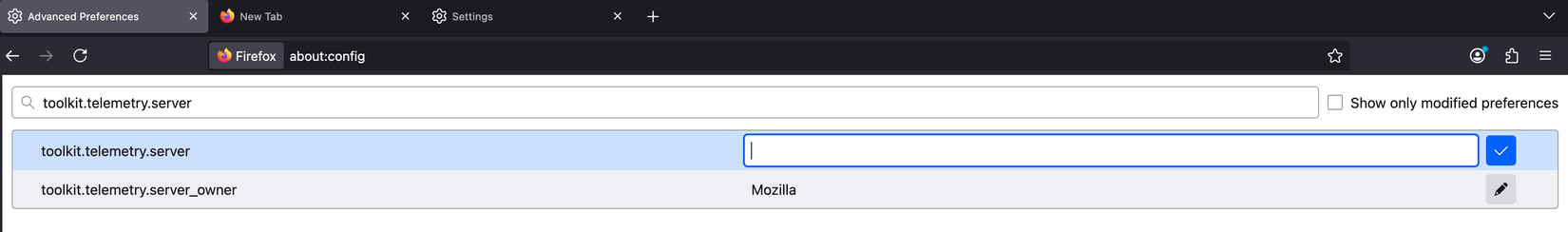
Additionally, check the toolkit.telemetry.server preference. If it contains any string, clear it out. This ensures Firefox no longer sends tracking data.
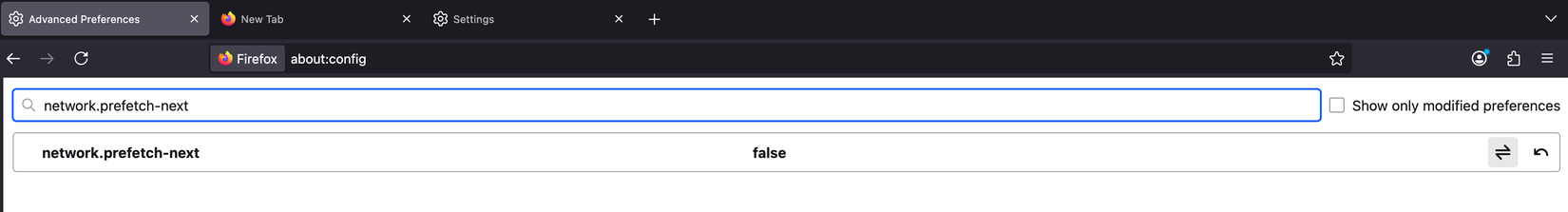
Stop Prefetching of Links
Firefox has a link prefetching feature that preloads pages in the background before you click them, allowing destination pages to open more quickly. While this can save time, the downside is that it uses extra bandwidth and system resources, which may slow down both your browsing experience and your device.
Once disabled, Firefox will only load pages when you actually click on them, helping conserve bandwidth and boosting performance by cutting out unnecessary background tasks.
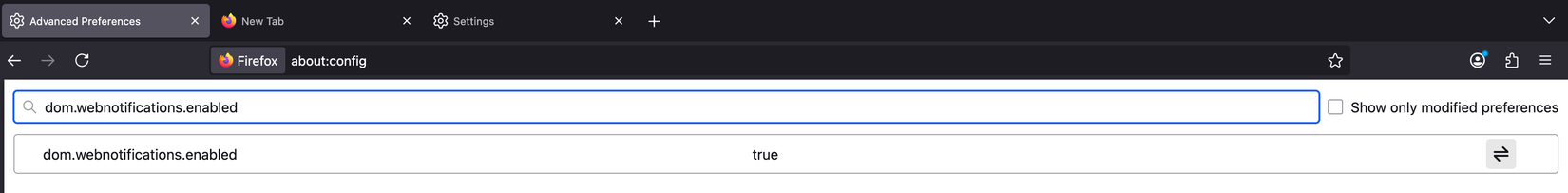
Disable Web Notifications and Push Services
Like other browsers, Firefox often lets websites request permission to send you push notifications, such as news alerts or promotional messages. If you accidentally allow an unknown site, you may end up with constant spam and distractions. These background push services also consume system resources and create potential privacy risks.
Thanks to the flexibility Firefox offers, you have the freedom to tailor it into the browser you truly want. Its config settings let you minimize distractions, remove unnecessary extras, and focus on features that make browsing faster and more efficient. If you find the browser annoying, apply these tweaks—you’ll notice the difference just as I did.
Source: https://www.howtogeek.com/firefox-config-settings/